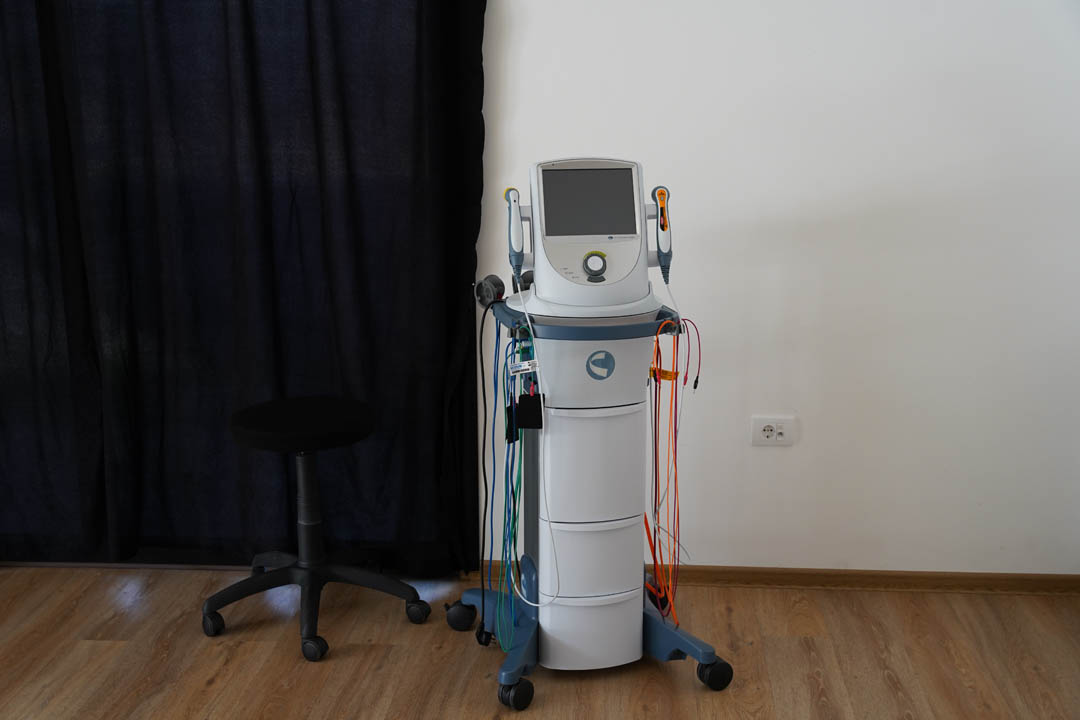
Possible side effects and precautions of magnetic therapy
Although magnetic therapy is considered an extremely low-risk method, there are rare situations when temporary bodily reactions may occur. These typically include mild fatigue, increased sleepiness, or brief dizziness after treatment, especially in individuals sensitive to changes in the nervous or circulatory systems.
Certain medical conditions make this therapy inadvisable. These include neurological disorders such as epilepsy, electronic implants (e.g., pacemakers), active oncological diseases, and specific heart problems. Therefore, a professional assessment is essential prior to therapy to ensure safe and effective application.
When is magnetic therapy recommended?
This procedure is widely used in treatments aiming to reduce pain, stimulate natural recovery processes, and accelerate the return of functionality. It is particularly recommended in cases where other methods have not provided desired outcomes or when a gentler approach is sought.
It is most commonly applied in rehabilitation for:
- Joint discomfort in shoulders, hips, or knees.
- Degenerative changes in the spine
- Disorders of bone mineral density.
- Conditions following casts, surgeries, or orthopedic procedures.
- Strains, bruises, and painful muscle points.
- Diseases affecting mobility and flexibility.
In some cases, magnetic therapy is also utilized as a supplement to conventional therapies, to accelerate results and facilitate daily life for those dealing with prolonged conditions.
Who is magnetic therapy recommended for?
Magnetic therapy is especially suitable for individuals seeking support in preserving mobility and daily functionality without placing additional strain on the body.
It is recommended for:
- Older adults who wish to maintain musculoskeletal health.
- Patients in postoperative recovery to shorten rehabilitation time.
- Individuals with reduced physical activity looking to stimulate natural bodily processes.
- Those seeking to alleviate chronic discomfort without additional medication.
- Athletes and recreational participants recovering from strain or injuries.
Due to its flexibility and high safety level, magnetic therapy can be adapted to individuals with complex diagnoses, as well as those looking for preventive care and quality support for everyday functionality.
Benefits of magnetic therapy
In addition to its primary therapeutic effect, magnetic therapy offers numerous additional advantages, making it suitable for various user needs and ages:
- Safe for long-term use, without unwanted side effects.
- Requires no physical contact, ideal for sensitive or painful areas.
- Treatments are quiet and relaxing, without noise or stress.
- Suitable for users with limited mobility, as it is performed in lying or sitting positions.
- Can serve as preparation for other therapies by relaxing tissue and improving circulation.
- Supports a general sense of vitality, particularly in older adults.
These advantages make magnetic therapy particularly beneficial within rehabilitation programs requiring gentle yet effective bodily support.
Experience and practice in magnetic therapy application
Based on the experience in our center, magnetic therapy has shown to significantly reduce pain and swelling after just a few treatments, particularly among patients with chronic conditions or slowed recovery following surgeries.
Patients report treatments as pleasant and relaxing. An additional motivating factor is the feeling of relief and improved mobility experienced after each series.
Magnetic therapy pricing
For more information about pricing, available appointments, and expert recommendations, please visit our Contact page, where you’ll find the phone number and all necessary details.
The price of magnetic therapy may vary depending on the type of condition, duration of individual treatment sessions, and whether it’s applied as a standalone treatment or part of a broader rehabilitation plan.
In addition to magnetic therapy, Rehab Senior center offers other therapeutic methods, which can be combined as needed, such as physical therapy, kinesiotherapy, ultrasound therapy, electrotherapy, hydrotherapy, massages, and group exercises, depending on each user’s needs and goals.